
My latest posts can be found here: Previous blog posts:
Additionally, some earlier writings: |
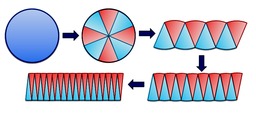
Starting with a circle ...
Someone asked if there was a similar visualisation of the volume of a sphere, or the surface area of a sphere, and that started me thinking. We know that for a circle, for some reason, the circumference is the derivative of the area, and similarly for the sphere, the surface area is the derivative of the volume, and I wondering about visualisations of that, and related things. This is what I came up with - I'd welcome comment, thoughts, and feedback.
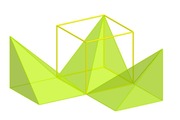
Consider one vertex of the cube, which is adjacent to three faces. For each of the other three faces, we have a square-based pyramid with the face as the base, and the chosen vertex as the apex. There are several ways to see that, and to be honest, the absolute best is to make a model for yourself. However, in lieu of that, here's a picture:
You can play with an interactive version of that here:
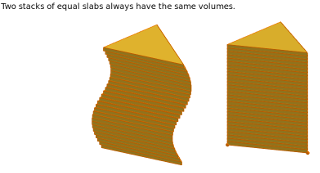
This is called "Cavalieri's principle" and you can play with an interactive version of that here:
So we can convert our non-right pyramid into a square-based right pyramid. Thus we've shown that a square-based pyramid of base area 1 and height 1 has a volume of $1/3$. We can scale or transform each slice. If we choose a new shape, we can convert each square slice into that new shape, and provided the area of the slice remains the same, we don't change the volume. Similarly, we can scale each slice, and the volume changes by the same scale. So for example, replace each square with a disk of the same area. The result is then a cone with the same volume. Now scale each disk down to half the area. The result is still a cone, but now with half the volume. We have halved the area of the base, so we have halved the volume of the cone. This shows that the volume is still $1/3$ times the height (which is still 1) times the area of the base. Finally, consider the height. If we scale vertically then we change the volume by the scaling factor. Consider doubling the number of slices. In doing so we double the height, and double the volume. Alternatively, if we want to finish with height $h$ then start with a cube of size $h^3$. Then the area of the base of the square-based pyramid is $h^2$ and everything follows. I'll leave it to the (mythical) interested reader to work through the details, but it's all there. So we finally have the general formula that:
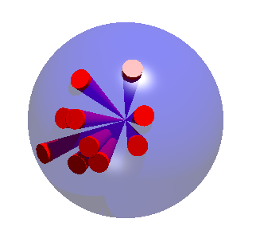
And now a piece of magic occurs ...Consider a sphere of radius $r$, and divide the surface into many, many small patches. Each small patch induces a "cone" to the centre, and each of those cones has a volume of $1/3$ times the radius times the area of the patch. So the total volume of the sphere is $1/3$ times $r$ times the total of the areas of the patches. But the total of the areas of the patches is the surface area of the sphere. So if the surface area of the sphere is $S$, then the volume of the sphere is $1/3$ times $r$ times $S$. Now we need the surface of the sphere. That is given to us by the Archimedes Hat Box Theorem (see the box on the right), and is $4{\pi}r^2.$
Another observationIf the surface area of a sphere is $4{\pi}r^2$ then when we increase the radius by a tiny amount, $dr$, the volume increases by the volume of the "egg shell" created, which is $4{\pi}r^2.dr$. We can then get the volume of the sphere by taking lots and lots of "egg-shells", and we represent this as the integral $0$ to $r$ of $(4{\pi}r^2).dr$ So the volume is $\int_0^r 4{\pi}x^2.dx$ which we've seen to be $\frac{4}{3}{\pi}r^3$. Dividing through by $4\pi$ we therefore see that $\int_0^1 x^2 dx = 1/3$. We should be able to apply this "growing egg shell" argument to other shapes - the most obvious to try is the cube. Consider a cube of "radius" $r$, hence "diameter" $2r$, hence volume $(2r)^3=8r^3$. A small increase $dr$ in "radius" leads to an increase in volume of $6(2r)^2.dr$ (six faces, each of size $2r$ by $2r$ and thickness $dr$). So the volume is $\int_0^r 6(2r)^2 dr$ which is $\int_0^r 24r^2 dr$. This evaluates to $24(1/3)r^3 = 8r^3$, just as above. So the technique works for the cube as well.
For extra credit ...Anyone for the volume of a tetrahedron?
My thanks to ...... Philipp Reinhard, Robert Low, JordiGH@Mathstodon.xyz, Andrea Della Corte, and others to be included when (or if!) they give their permission, for reading and commenting on earlier versions of this post.
Send us a comment ...
|




 Suggest a change ( <--
What does this mean?) /
Send me email
Suggest a change ( <--
What does this mean?) /
Send me email